What is induction?
Before you can understand induction cooking, you need to understand
induction.
And the first thing you need to know is that "induction" is a
shortened way of saying "electromagnetic induction." In a
nutshell, induction means generating
electricity using
magnetism. It stems from the simple fact that
electricity and magnetism aren't separate, unconnected things (as we
originally learn in school) but two different aspects of the same
underlying phenomenon:
electromagnetism.
How induction cooking works
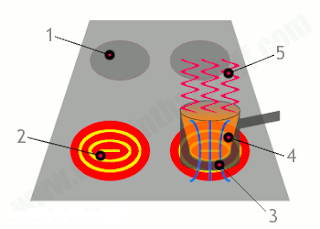
- An induction cooker looks much the same as any other ceramic
cooktop, usually with distinct zones where you can place your pots and
pans.
- Inside each cooking zone, there's a coil of metal. When you turn on
the power, an alternating current flows through the coil and produces an
invisible magnetic field above, below, and all around it. Unless
there's a pan on the cooking zone, no heat is produced: the cooking zone
remains cold.
- Place a pan on the cooking zone and the magnetic field produced by
the coil (shown here with blue lines) penetrates the iron inside it.
- The magnetic field induces whirling electrical (eddy) currents inside the pan, turning into a heater ( (shown here in orange).
- Heat from the pan flows directly into the food or water inside it (by conduction).


Comments
Post a Comment